Learn more about
Brief Product Outline and Illustration
Questions about Cetrotide®?
Call our 24/7 toll-free support line at 1-800-387-8479 or submit your questions and comments using our online form.
Brief Product Outline and Illustration
Call our 24/7 toll-free support line at 1-800-387-8479 or submit your questions and comments using our online form.
A Cetrotide® injection guide is included in a pamphlet called Administration and Storage Instructions, which is available for download. The guides are offered in English or French—please click on the language of your choice. Should you require injection assistance in your language of origin, please call the Momentum patient program at 1-800-387-8479.
Cetrotide® is the brand name for the medication cetrorelix. Cetrotide® blocks the effect of a spontaneously released hormonehormonea chemical substance produced in one part of the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs in another part of the body, called gonadotropin-releasing hormone(GnRH)gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)a hormone released from the hypothalamus in the brain that signals the pituitary gland (also in the brain) to release other hormones called luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (which cause follicles to develop and release a mature egg from the ovary). GnRHgonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)a hormone released from the hypothalamus in the brain that signals the pituitary gland (also in the brain) to release other hormones called luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (which cause follicles to develop and release a mature egg from the ovary) controls the secretion of another hormone, called luteinizing hormonehormonea chemical substance produced in one part of the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs in another part of the body (LHluteinizing hormone (LH)a hormone release by the pituitary gland in the brain that acts in the ovary to stimulate ripening of the follicle and formation of the corpus luteum). LHluteinizing hormone (LH)a hormone release by the pituitary gland in the brain that acts in the ovary to stimulate ripening of the follicle and formation of the corpus luteum is the hormonehormonea chemical substance produced in one part of the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs in another part of the body that starts ovulationovulationrelease of an egg from the ovary (release of an egg) during the menstrual cyclemenstrual cycle (period)the monthly cycle of changes in the ovaries and the lining of the uterus, starting with the preparation of an egg for fertilization.[1]
Cetrotide® is provided as a white freeze-dried powder in a small glass container (vialviala small glass container for holding liquids) with a rubber stopper. The powder is dissolved in sterile water to make a liquid form of the medication that can then be injected. [1] The liquid medication should be used immediately after preparation. Each vialviala small glass container for holding liquids and syringesyringea hollow cylinder fitted with a sliding plunger that is used for injections when a needle is attached should be used only once.
Cetrotide® is available at a strength of 0.25 mg/vial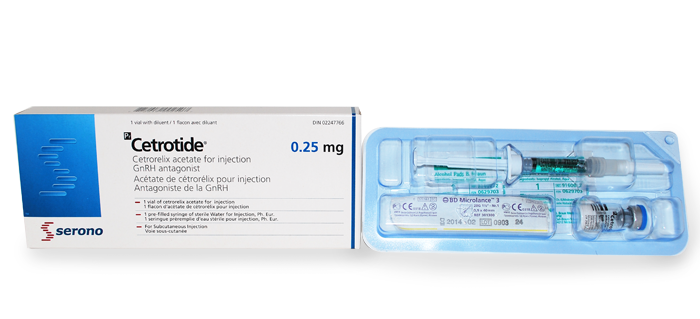 (note that mg stands for milligram, which is a unit of measure). [1]
(note that mg stands for milligram, which is a unit of measure). [1]
Cetrotide® 0.25 mg is available in a carton with a packaged tray containing: one glass vialviala small glass container for holding liquids of medication (white powder), one prefilled syringesyringea hollow cylinder fitted with a sliding plunger that is used for injections when a needle is attached with Sterile Water for Injection, one mixing needle, one injection needle, and two alcohol swabs. [1]
Your doctor will recommend the appropriate dose for you. [1]
When using daily dosing for ovarianovarianrelating to an ovary or the ovaries stimulation, 0.25 mg of Cetrotide® is given on either stimulation Daystimulation Daywhich numbered day of in vitro fertilization treatment during the stimulation phase when ovaries are stimulated to produce eggs 5 (morning or evening) or Day 6 (morning), and injections should continue once a day until the day that human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)a hormone produced in early pregnancy (released by the placenta after implantation of a fertilized egg) that keeps the corpus luteum producing other hormones that prevent menstruation is given.
Cetrotide® blocks the effect of a spontaneously occurring hormonehormonea chemical substance produced in one part of the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs in another part of the body called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)a hormone released from the hypothalamus in the brain that signals the pituitary gland (also in the brain) to release other hormones called luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (which cause follicles to develop and release a mature egg from the ovary). Because GnRHgonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)a hormone released from the hypothalamus in the brain that signals the pituitary gland (also in the brain) to release other hormones called luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone (which cause follicles to develop and release a mature egg from the ovary) controls the release of another hormonehormonea chemical substance produced in one part of the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs in another part of the body called luteinizing hormone (LHluteinizing hormone (LH)a hormone release by the pituitary gland in the brain that acts in the ovary to stimulate ripening of the follicle and formation of the corpus luteum), Cetrotide® therefore also suppresses the release of LHluteinizing hormone (LH)a hormone release by the pituitary gland in the brain that acts in the ovary to stimulate ripening of the follicle and formation of the corpus luteum and prevents the LHluteinizing hormone (LH)a hormone release by the pituitary gland in the brain that acts in the ovary to stimulate ripening of the follicle and formation of the corpus luteum surge that normally triggers ovulationovulationrelease of an egg from the ovary. [1]
Cetrotide® is used as part of the hormonehormonea chemical substance produced in one part of the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs in another part of the body treatment for controlled ovarianovarianrelating to an ovary or the ovaries stimulation, in which the ovariesovariesthe two sexual glands of the female where the eggs are stored and that produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone are stimulated to produce more than one egg. Cetrotide® is used to prevent premature ovulationovulationrelease of an egg from the ovary, [1] thus allowing doctors to delay and control the time of ovulationovulationrelease of an egg from the ovary so the eggs reach the level of development needed for fertilization.
When an ultrasoundultrasounda test used instead of X-rays to visualize the reproductive organs; for example, to monitor follicular development examination shows that enough folliclesfolliclessmall fluid-filled sacs in the ovary that contain the eggs released at ovulation; each month an egg develops inside the ovary in a follicle are ready, another drug human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)a hormone produced in early pregnancy (released by the placenta after implantation of a fertilized egg) that keeps the corpus luteum producing other hormones that prevent menstruation is injected to cause ovulationovulationrelease of an egg from the ovary at the desired time. [1]
You should not use Cetrotide® if you:
Before you use Cetrotide® let your doctor know if you are taking or have recently taken other medications, including those not requiring a prescription.[1]
As with all medication, there is a potential for side effects. Common side effects of Cetrotide® include: headache; injection site bruising, itching, swelling or redness; feeling sick (nausea). Rare cases of allergic reactions can occur (warm, red skin; itching [often in your groin or armpits]; red, itchy, raised areas [hives]; runny nose; fast or uneven pulse; swelling of your tongue and throat; sneezing; wheezing; serious difficulty breathing or dizziness). If you experience these symptoms, you may be having a possibly serious, life-threatening allergic reaction to the medicine. If you notice any of the side effects above, stop using Cetrotide® and seek immediate medical attention. [1]
During or following hormonal stimulation of the ovariesovariesthe two sexual glands of the female where the eggs are stored and that produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone, ovarianovarianrelating to an ovary or the ovaries hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSSovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)OHSS is caused when the ovaries become overstimulated by the various hormones that cause follicular development; there is a sudden ovarian enlargement accompanied by fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity and this may occur with or without pain, and with or without accumulation of fluid in the lungs) may develop. OHSSovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)OHSS is caused when the ovaries become overstimulated by the various hormones that cause follicular development; there is a sudden ovarian enlargement accompanied by fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity and this may occur with or without pain, and with or without accumulation of fluid in the lungs is a rare condition that occurs when too many folliclesfolliclessmall fluid-filled sacs in the ovary that contain the eggs released at ovulation; each month an egg develops inside the ovary in a follicle grow and cause abdominal discomfort or pain, nausea, diarrhea, and sometimes difficulty in breathing. In extreme cases, hospitalization is necessary. OHSSovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)OHSS is caused when the ovaries become overstimulated by the various hormones that cause follicular development; there is a sudden ovarian enlargement accompanied by fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity and this may occur with or without pain, and with or without accumulation of fluid in the lungs is potentially very serious, but can be avoided by careful monitoring by your doctor. [1]
Call your doctor if you have any side effects, including ones not mentioned here or if you are unsure about the effect of this medicine. [1]
CETROTIDE should be stored by the patient between 2 – 8 °C (in a refrigerator). However, storage at up to 30°C for a maximum of 3 months is also allowed. Do not freeze. Keep the packaged tray in the outer carton in order to protect it from light. Store the medicine out of the reach of children.[1]
Do not use the Cetrotide® powder or the prefilled syringesyringea hollow cylinder fitted with a sliding plunger that is used for injections when a needle is attached after the expiration date, which is printed on the labels and on the carton. After expiry, dispose of the vialviala small glass container for holding liquids and the syringesyringea hollow cylinder fitted with a sliding plunger that is used for injections when a needle is attached properly.[1]
Use the syringesyringea hollow cylinder fitted with a sliding plunger that is used for injections when a needle is attached and needles only once. Dispose of the syringesyringea hollow cylinder fitted with a sliding plunger that is used for injections when a needle is attached and needles immediately after using them by putting them in a disposal container or a puncture-proof container with a lid that fits firmly. [1]